41 atp diagram labeled
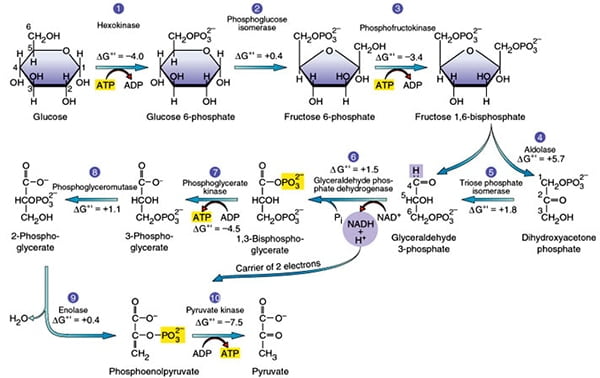
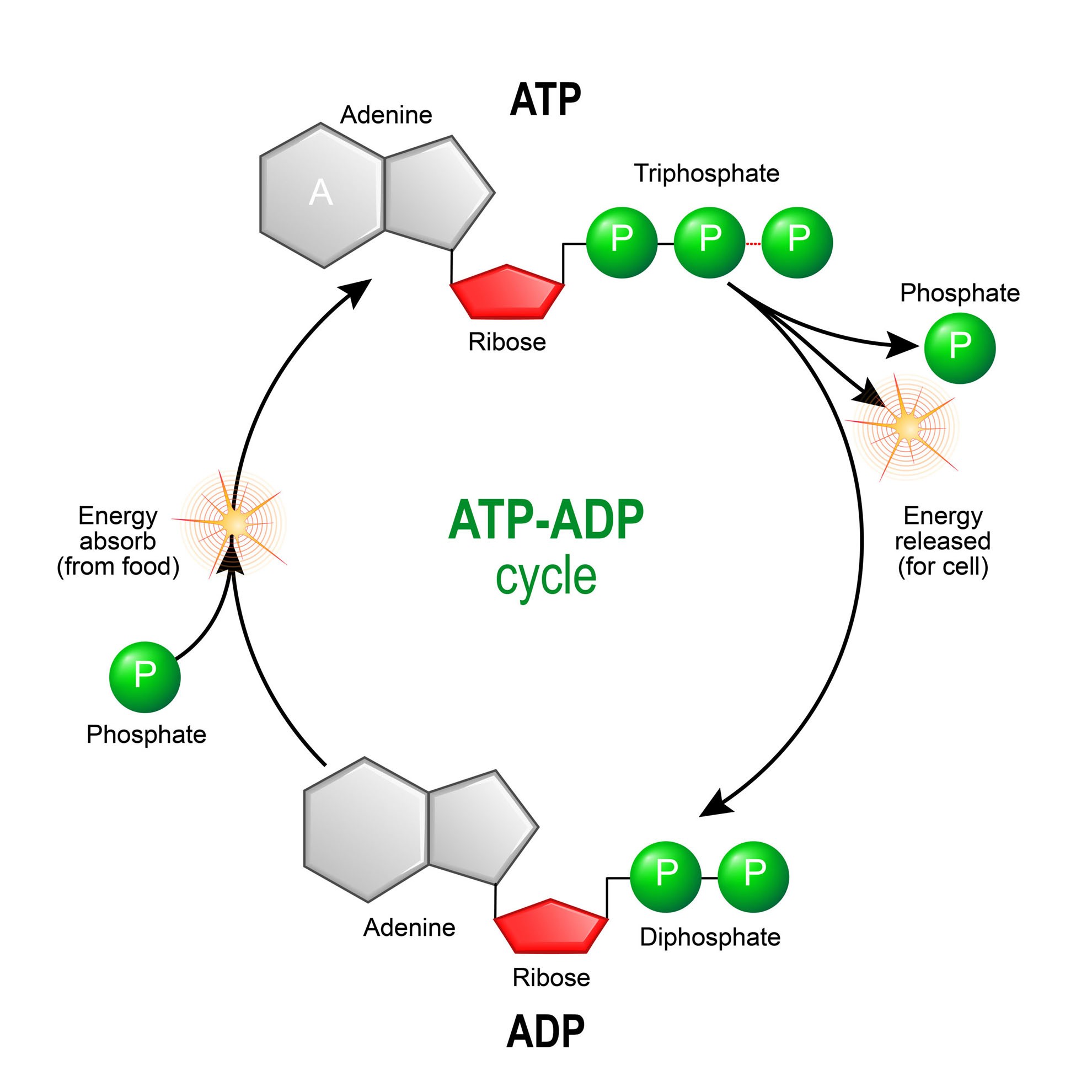
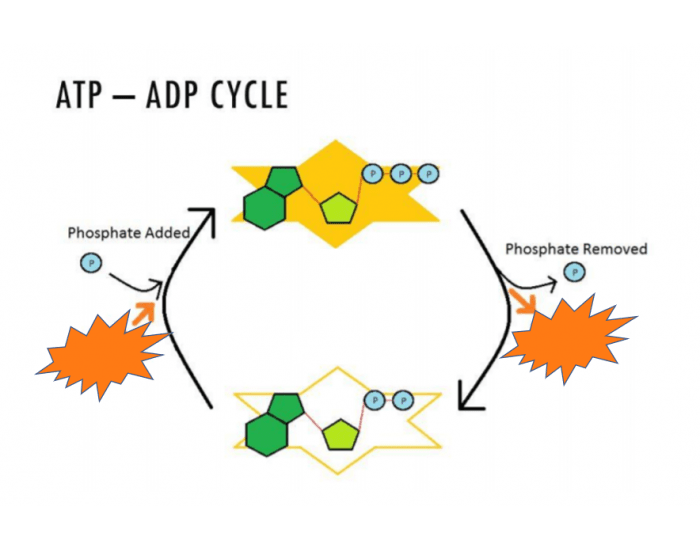
ATP and ADP Cycle diagram to label and fill the blanks.docx... Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is the energy molecule used by all cells to do work. It is a nucleotide consisting of a nitrogen-containing base (adenine, thymine, cytosine, or guanine), a 5-carbon sugar, and 3 phosphate groups. ATP is able to store and transport chemical energy within cells. Diagram of Skeletal Muscle - BYJUS Diagram of Skeletal Muscle. Skeletal muscles are voluntary and striated in nature. They are responsible for the movement of appendages and locomotion. Skeletal muscle is formed by 75% of water and 25% of solids. The solid components include proteins and other organic and inorganic substances. All the components of the skeletal muscle contribute ...
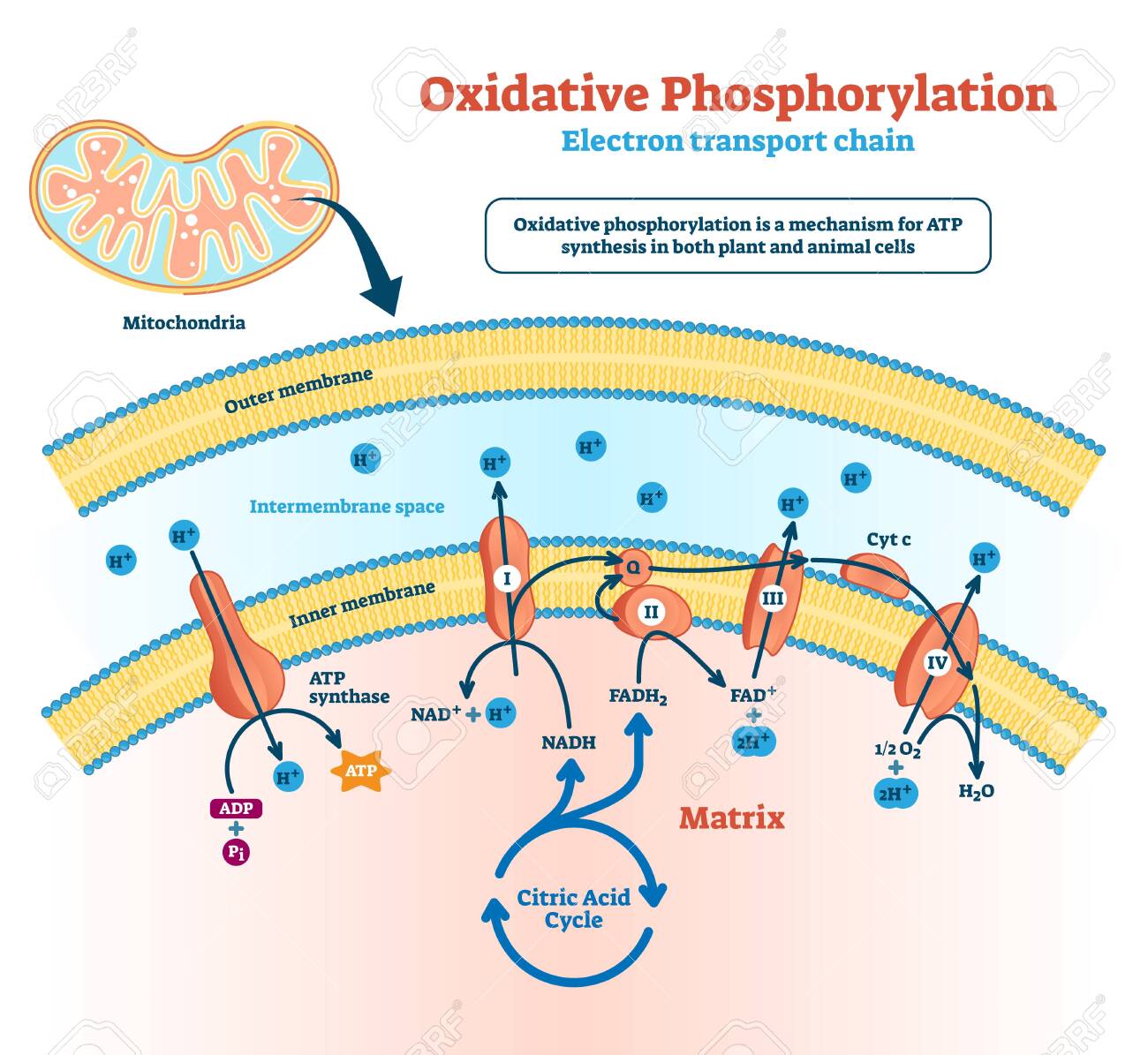
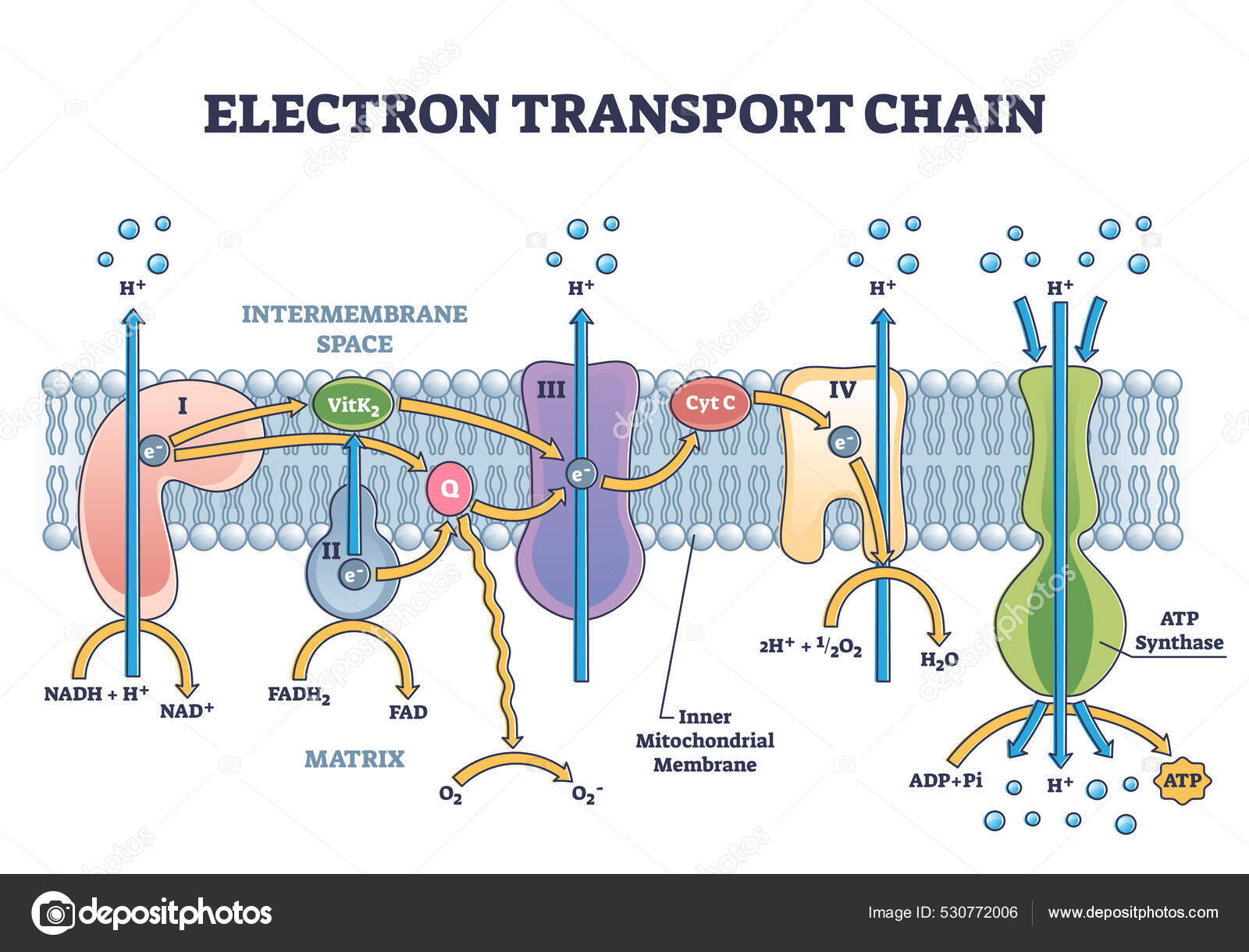
ATP Synthase: Structure and Mechanism | Cell Biology | Biology ADVERTISEMENTS: After reading this article you will learn about the structure and mechanism of ATP synthase, with the help of suitable diagrams. Boyer and Walker received the Nobel Prize in 1997 for elucidating the mechanism of ATP synthase. This is all-important reactions in which the proton-motive force, produced by proton translocation, is coupled to the […]
Atp diagram labeled
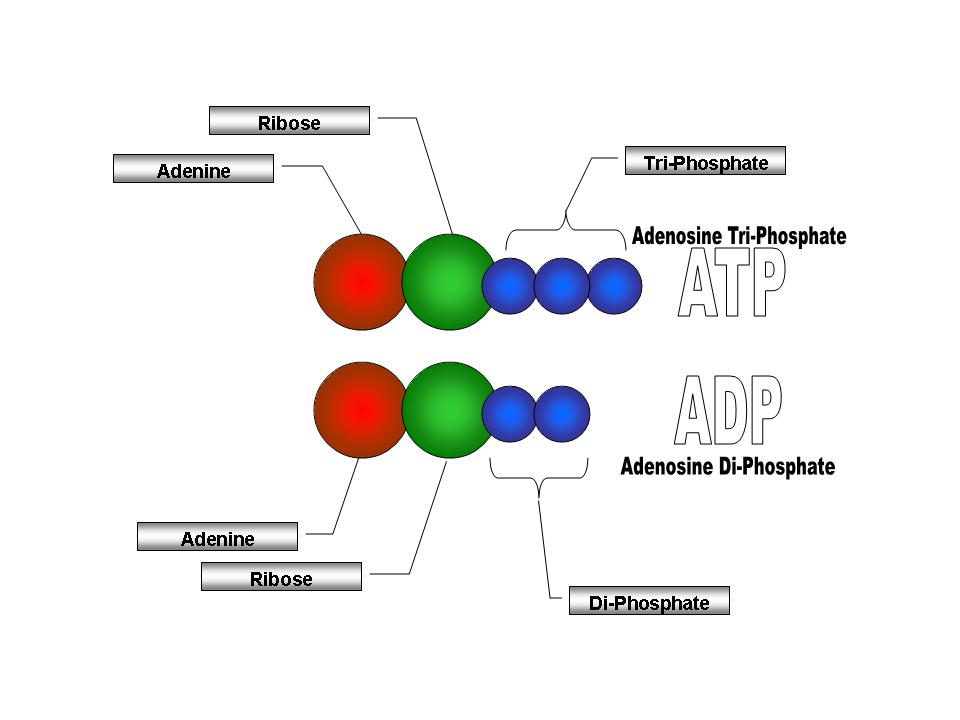
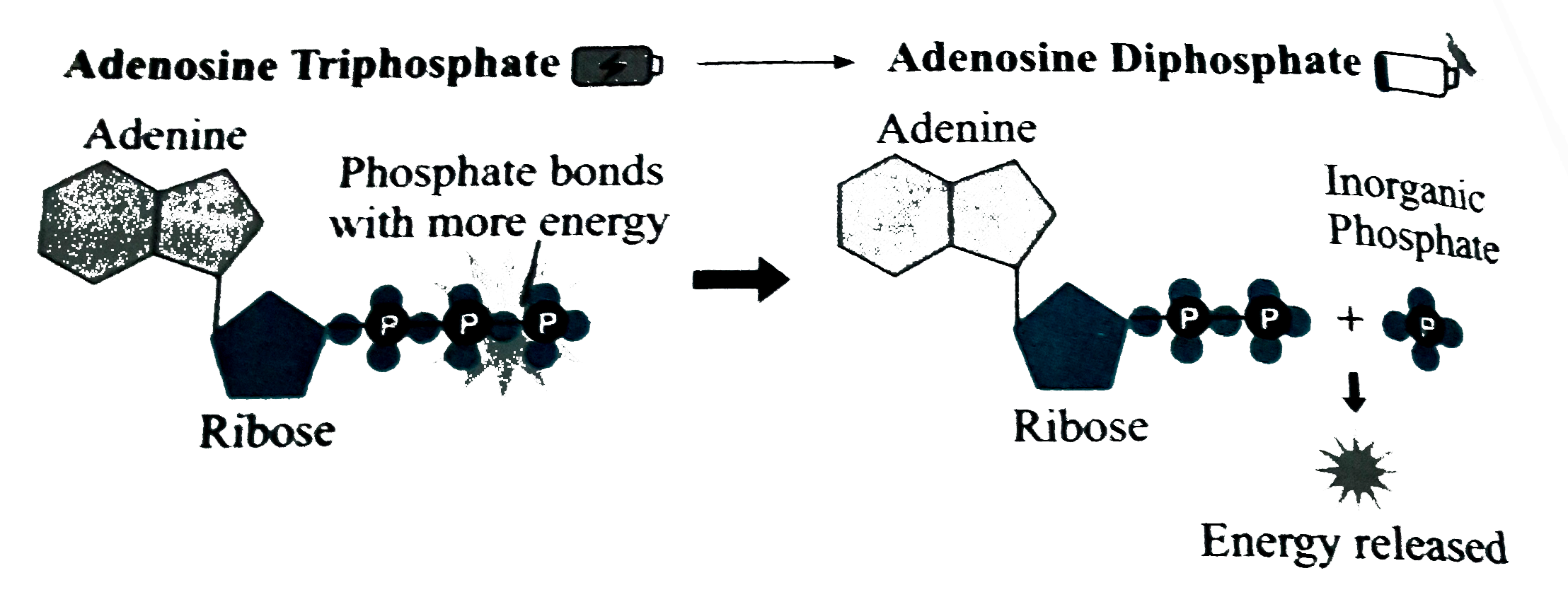
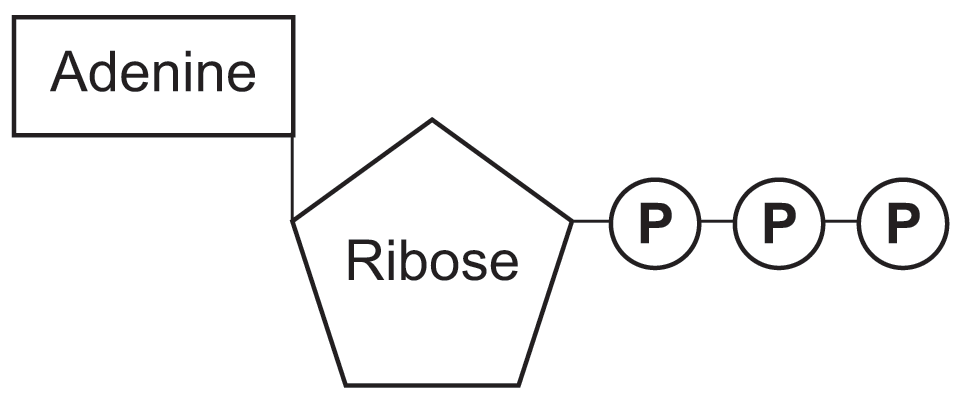
6. Cell-Energy-Web Quest-Student-Handout - Name: Per: ATP ... The full name of ATP is Adenosine triphosphate. Label the ATP Diagram to the right with what each shape represents. ATP is a molecule in the cell that allows for quick and easy energy when needed by the cells organelles. ATP is a type of molecule that releases energy when the chemical bonds are broken between two phosphate groups. Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP) - Definition, Structure, & Diagram Adenosine triphosphate, abbreviated ATP, is an organic molecule that supplies energy for all cellular activities in plants, animals, and lower organisms. These molecules capture the stored chemical energy of digested foods and later release it for various cellular processes. Structure of ATP - Learn Insta ATP is a nucleotide that consists of three main structures: the nitrogenous base, adenine; the sugar, ribose; and a chain of three phosphate groups bound to ribose. The phosphate tail of ATP is the actual power source which the cell taps.
Atp diagram labeled. Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP) - Definition, Structure and Function Adenosine triphosphate, also known as ATP, is a molecule that carries energy within cells. It is the main energy currency of the cell, and it is an end product of the processes of photophosphorylation (adding a phosphate group to a molecule using energy from light), cellular respiration, and fermentation. All living things use ATP. Solved Chemiosmosis and ATP Synthese 5. Label the ATP | Chegg.com Label the ATP synthase on Diagram 6. 6. Describe how the proton (H') gradient is used to make ATP 7. What two molecules bring chemical energy from the light reactions to the next stage of photosynthesis, the Calvin cycle? PART 6: CALVIN CYCLE 1. Label Diagram 7 with the three phases of the Calvin cycle. Diagram 7 Phase 1 ATP Diagram | Quizlet a cycle that converts ADP into ATP & ATP releases energy and turns into ADP. Students also viewed. F1 Unité 2 CDO1 School Supplies/30-60. 20 terms. nyjohnston Teacher. Biochemical Reactions and Enzymes. 23 terms. Allegra_Weinstein Teacher. Biotechnology. 13 terms. Deb_Acree Teacher. Biochemistry - Biology. How Does ADP Become ATP? Cycle, Structure, and Function - Study.com ATP Structure The molecular structure of ATP is comprised of: 1 adenine: A purine base 1 ribose: A 5-carbon simple sugar 3 phosphate molecules: The majority of the ATP's energy is also stored...
Solved Chemiosmosis and ATP Synthose 5. Label the ATP | Chegg.com PART 6: CALVIN CYCLE 1. Label Diagram 7 with the three phases of the Calvin cycle. Diagram 7 Phase 1 5. Label the ATP synthase on Diagram 6 Show transcribed image text Expert Answer Transcribed image text: Chemiosmosis and ATP Synthose 5. Label the ATP synthase on Diagram 6. 6. Describe how the proton ( ) gradient is used to make ATP. 7. ATP Synthase Diagram | Quizlet Term The diffusion of H+ ions through membrane protein, ATP synthase powers production of ATP Location Term H+ ions diffuse down thier concentration gradient (electrochemical energy) back into the matrix Location Term H+ ions must pass thru channedl protein (ATP synthase) Location Term Atp Diagram Stock Illustrations - 142 Atp Diagram Stock Illustrations ... Download 142 Atp Diagram Stock Illustrations, Vectors & Clipart for FREE or amazingly low rates! New users enjoy 60% OFF. 206,080,845 stock photos online. ATP: How It Works, How It's Made, and Why It's Important ATP is made of a nitrogen base (adenine) and a sugar molecule (ribose), which create adenosine, plus three phosphate molecules. If adenosine only has one phosphate molecule, it's called adenosine monophosphate (AMP). If it has two phosphates, it's called adenosine diphosphate (ADP).
[Solved] 8. Label this ATP diagram. a. b. C. P P P | Course Hero Label this ATP diagram. a. b. C. P P P. Get more out of your subscription* Access to over 100 million course-specific study resources; 24/7 help from Expert Tutors on 140+ subjects; Full access to over 1 million Textbook Solutions; Subscribe *You can change, pause or cancel anytime. Where can I see a labeled diagram of ADP and ATP? - Answers Try the two links below for labeled diagrams of ATP. The link for ADP has no labels, but you can recognize the components after looking at the ATP images. Wiki User ∙ 2008-12-03 03:40:05... ATP Diagram - Labelled diagram - Wordwall ATP Diagram - Labelled diagram Price Plans Language Adenosine, Ribose, Phosphate #1, Phosphate #2, Phosphate #3, A little bit of energy, Some energy, A lot of energy. ATP Diagram Share by Mbarfiel Science Like Edit Content More Leaderboard Switch template Interactives A Well-labelled Diagram Of Animal Cell With Explanation - BYJUS A Well-labelled Diagram Of Animal Cell With Explanation Biology Biology Article Diagram Of Animal Cell Diagram Of Animal Cell Animal cells are eukaryotic cells that contain a membrane-bound nucleus. They are different from plant cells in that they do contain cell walls and chloroplast.
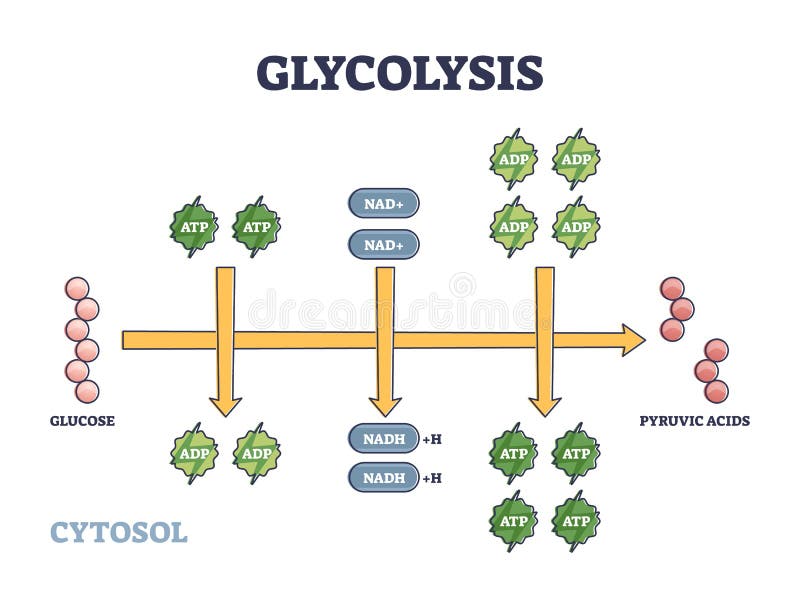
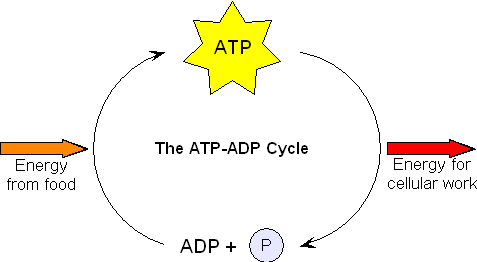
ATP cycle and reaction coupling | Energy (article) | Khan Academy Adenosine triphosphate, or ATP, is a small, relatively simple molecule. It can be thought of as the main energy currency of cells, much as money is the main economic currency of human societies. The energy released by hydrolysis (breakdown) of ATP is used to power many energy-requiring cellular reactions. Image credit: OpenStax Biology.
The Structure of an Atom Explained With a Labeled Diagram Basic Diagram of an Atom. Most of an atom is just empty space and consists of a positively charged nucleus of protons and neutrons surrounded by a cloud of negatively charged electrons. The center of an atom is the nucleus and one or more electrons surrounding the nucleus. When one says an atom is electrically neutral, it means that the number ...
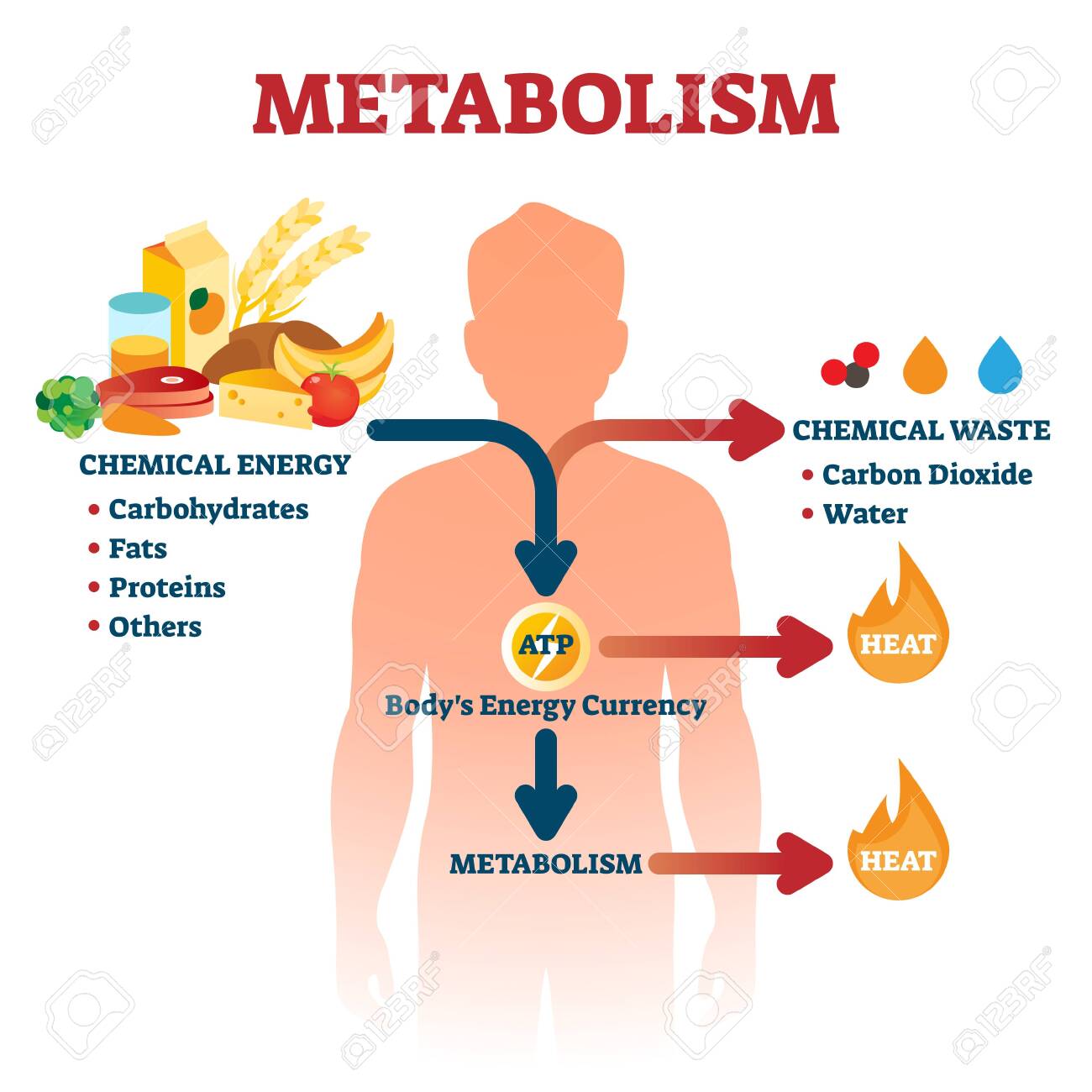
Adenosine-5'-triphosphate | C10H16N5O13P3 - PubChem Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is the nucleotide known in biochemistry as the "molecular currency" of intracellular energy transfer; that is, ATP is able to store and transport chemical energy within cells. ATP also plays an important role in the synthesis of nucleic acids. The total quantity of ATP in the human body is about 0.1 mole.
1.6.1 The Structure of ATP - Save My Exams Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is the energy-carrying molecule that provides the energy to drive many processes inside living cells. ATP is another type of nucleic acid and hence it is structurally very similar to the nucleotides that make up DNA and RNA. It is a phosphorylated nucleotide. Adenosine (a nucleoside) can be combined with one, two or ...
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) | Definition, Structure, Function, & Facts ATP is a nucleotide that consists of three main structures: the nitrogenous base, adenine; the sugar, ribose; and a chain of three phosphate groups bound to ribose. The phosphate tail of ATP is the actual power source which the cell taps.
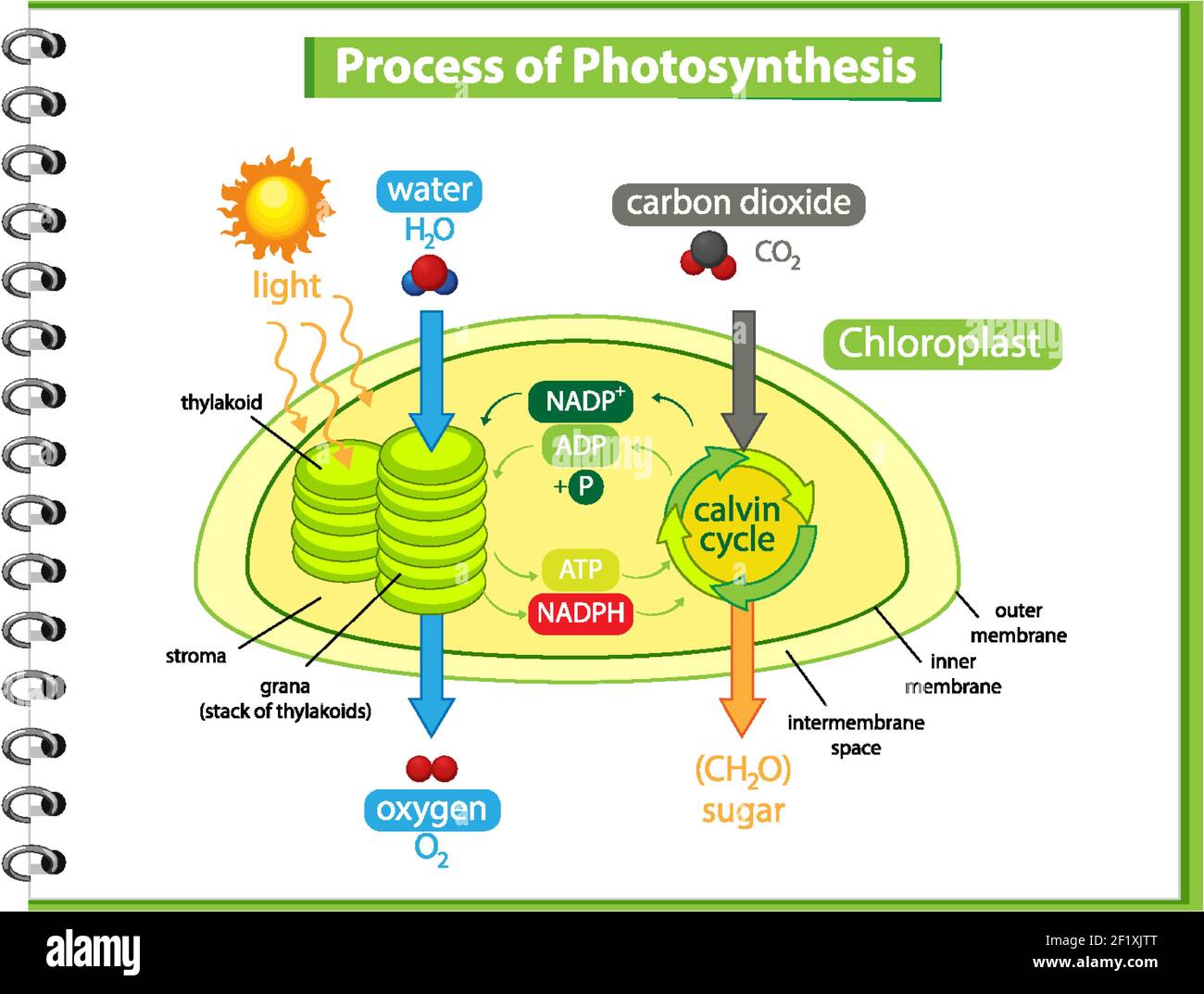
Photosynthesis Diagram: From Beginning To End - Science Trends The cells of the plant will take in carbon dioxide, water, and sunlight and convert it into usable energy through photosynthesis. Given that carbon dioxide and water are the necessary ingredients for the creation of glucose, or sugar, the chemical equation for photosynthesis can be represented in this form: 6 CO2 + 6 H2O → C6H12O6 + 6 O2.
60+ Labeled Muscle Diagram Illustrations, Royalty-Free Vector Graphics ... Labeled diagram with brain sections and its functions with senses. Regions with olfactory, optic, abducent, facial and vagus parts. stages of atherosclerosis stages of atherosclerosis. Detailed illustration. Healthy artery and unhealthy arteries. Developing of plaque from fatty streak to Calcification and thrombosis. cardiovascular disease.
What are three parts of an ATP molecule? | Socratic Adenine, Ribose, and three Phosphate groups. Explanation: ATP molecules are used by all living organism as energy to carry out life functions. Also notable, ATP stands for Adenosine Triphosphate. This molecule is composed of three parts: Adenine Ribose Three Phosphate Groups Here is a picture: Answer link
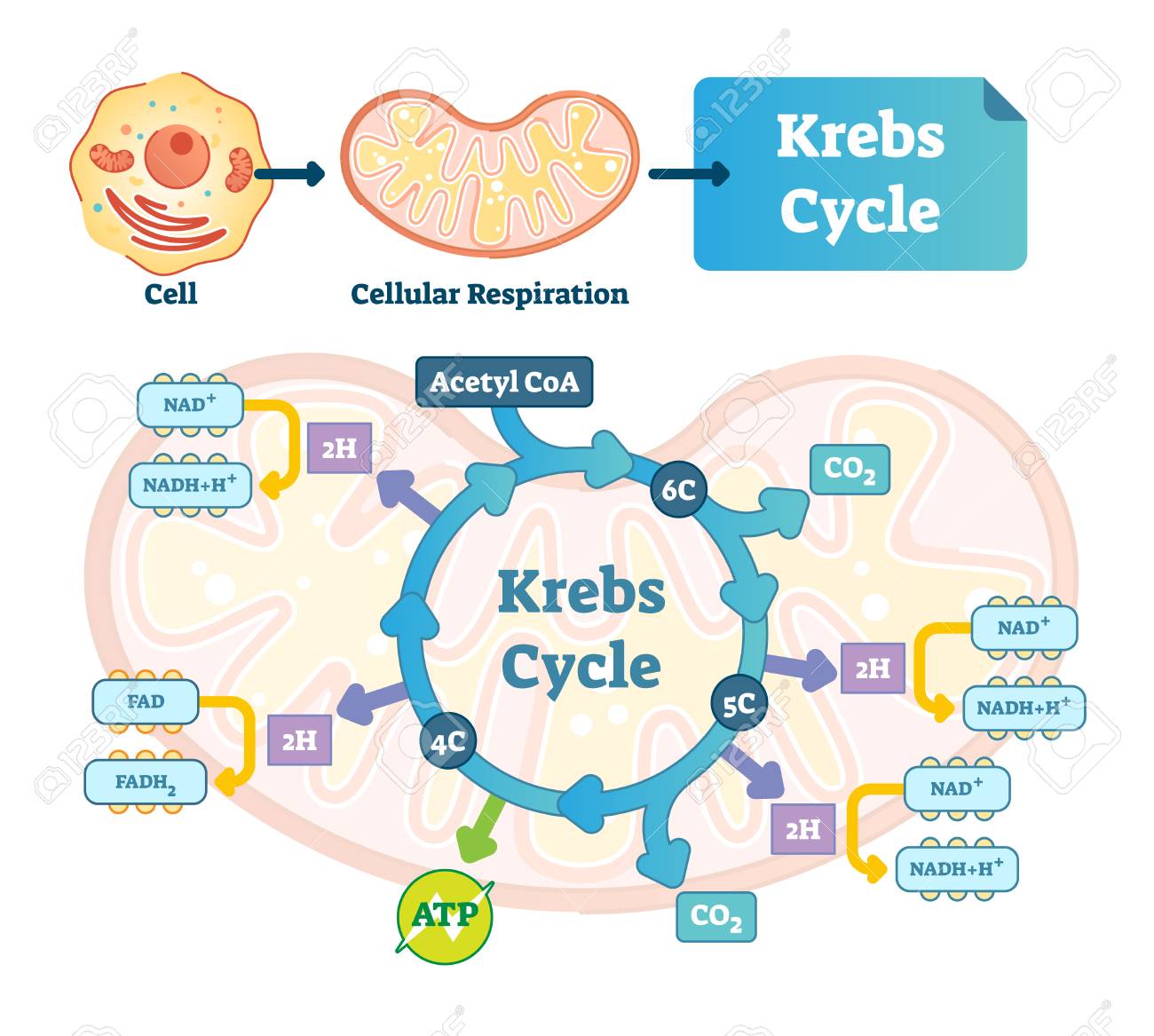
Cellular Respiration Diagram - Biology Wise The energy released is in the form of ATP molecules that are used to carry out various functions of the cell. The cellular respiration equation is as follows: C6H12O6 + O2 ――> H2O + CO2 + 36ATP. The following diagram of cellular respiration will give a better understanding of this process.
CBSE Class 11-science Answered - TopperLearning Draw a well-labelled diagram indicating the synthesis of ATP in mitochondria. Asked by Topperlearning User | 13 Jun, 2016, 02:33: PM Expert Answer Synthesis of ATP in mitochondria: Answered by | 13 Jun, 2016, 04:33: PM Concept Videos This video discusses the mechanism for synthesis of ATP during respiration.
Formula used for ATP calculation - IBM The calculation of ATP is governed by a pretty simple formula. ATP= Total Supplies - Total Demand in a given date range. Now let us look into the constraints involved in this formula. We shall look into the Global Inventory Visibility screen which partly governs the calculation. See attached image.
Structure of ATP - Learn Insta ATP is a nucleotide that consists of three main structures: the nitrogenous base, adenine; the sugar, ribose; and a chain of three phosphate groups bound to ribose. The phosphate tail of ATP is the actual power source which the cell taps.
Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP) - Definition, Structure, & Diagram Adenosine triphosphate, abbreviated ATP, is an organic molecule that supplies energy for all cellular activities in plants, animals, and lower organisms. These molecules capture the stored chemical energy of digested foods and later release it for various cellular processes.
6. Cell-Energy-Web Quest-Student-Handout - Name: Per: ATP ... The full name of ATP is Adenosine triphosphate. Label the ATP Diagram to the right with what each shape represents. ATP is a molecule in the cell that allows for quick and easy energy when needed by the cells organelles. ATP is a type of molecule that releases energy when the chemical bonds are broken between two phosphate groups.


















Post a Comment for "41 atp diagram labeled"